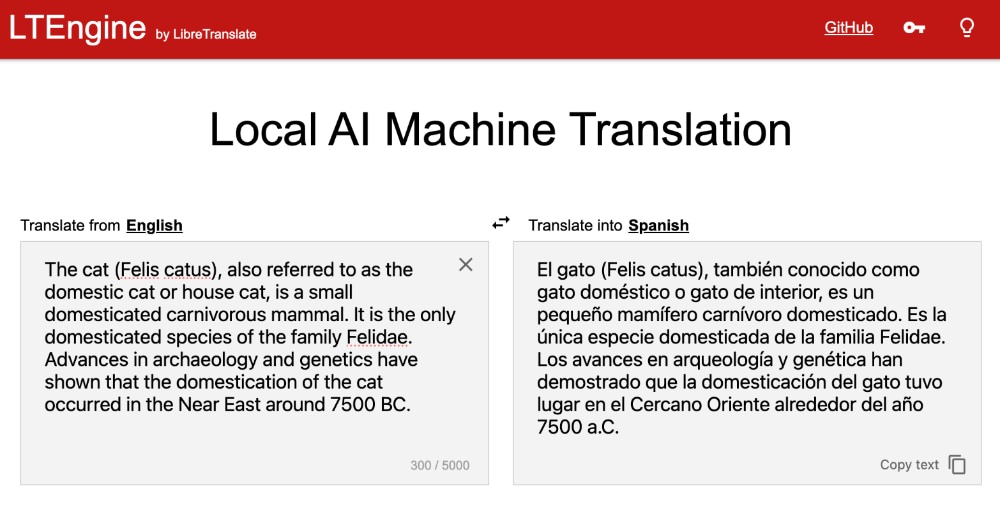
Over the years, a choice had to be made between utilizing cloud-based tools such as **[Google Translate](https://translate.google.com)** or [DeepL](https://www.deepl.com/en/translator), and opting for open-source, privacy-conscious tools that sometimes fell short in terms of quality. Thankfully, due to the rapid progress in AI and machine learning, this trade-off is no longer required.
Introducing **[LTEngine](https://github.com/LibreTranslate/LTEngine?tab=readme-ov-file)**. This innovative tool is an AI-driven enhancement of the well-known [LibreTranslate](https://github.com/LibreTranslate/LibreTranslate) project. It offers the same top-notch translation accuracy you would expect from major commercial services but with a significant distinction: all operations take place locally on your own device.
This tool is ideal for those who value privacy yet seek high-quality translations for various purposes such as business documents, personal messages, and more. Let’s delve into how you can implement this solution.
As of now, LTEngine is actively being developed and does not have a single executable file available for installation. Therefore, the following prerequisites are essential to set up your environment:
* **[Rust](https://rust-lang.org)**: The main programming language for the LTEngine server.
* **[Clang](https://clang.llvm.org/)**: A front-end compiler for C/C++ to compile native dependencies.
* **[CMake](https://cmake.org/)**: A versatile build system crucial for configuring the native build process.
* **A C++ Compiler**: Either g++ (Linux/macOS) or MSVC (Windows) for the final compilation of native bindings.
To verify if these tools are already present on your system, access your terminal or command prompt and execute the provided commands:
| **Tool** | **Check Command** | **Installation Recommendation** |
| — | — | — |
| **Rust** | `rustc –version` | Install using [rustup](https://rustup.rs), the recommended toolchain manager for all platforms. |
| **Clang** | `clang –version` | On Linux, install by running `sudo apt install build-essential clang`. On macOS, use `xcode-select –install`. For Windows, install the Desktop development with C++ workload through the Visual Studio Build Tools installer. |
| **CMake** | `cmake –version` | On Linux, install via `sudo apt install cmake`. On macOS, use `brew install cmake`. For Windows, download CMake from [the official installer](https://cmake.org/download/). |
If each tool displays a version number upon execution, you are ready to proceed!
With the prerequisites fulfilled, it is now time to set up LTEngine. Initially, clone the repository by running:
“`
git clone https://github.com/LibreTranslate/LTEngine –recursive
“`
Then navigate to the directory using:
“`
cd LTEngine
“`
Subsequently, proceed with building the project based on your system’s GPU by choosing one of these commands:
“`
# For Metal (macOS)
cargo build –features metal –release
# For CUDA and Vulkan (Linux/Windows)
cargo build –features cuda,vulkan –release
“`
This step may take a while as it compiles essential components. Once completed, you will find the compiled binary in the `target/release` directory. Now, launch the server by executing the built binary:
“`
./target/release/ltengine
“`
LTEngine comes pre-equipped with support for [Gemma3](https://deepmind.google/models/gemma/gemma-3/). To download the model, append `-m` followed by the model name like so:
“`
./target/release/ltengine -m gemma3-1b
“`
The Gemma3 1B model will be downloaded – a compact model suitable for testing due to its lower computational and memory requirements despite having less translation accuracy compared to larger models. For practical application, consider employing larger models such as Gemma3 4B or 16B if your hardware permits.
Once the model is acquired, commence translating text by sending requests to the server’s API endpoints at `http://localhost:5050/translate`.
LTEngine provides a RESTful API to handle translation requests. Submit a POST request to `/translate` containing the text for translation and desired target language:
“`
curl -X POST “http://localhost:5050/translate” -H “Content-Type: application/json” -d ‘{
“q”: “Hello, world!”,
“source”: “en”,
“target”: “es”
}’
“`
This request translates “Hello world!” from English to Spanish with the server responding with the translated text:
“`
{
“translatedText”: “¡Hola, mundo!”
}
“`
You can also allow LTEngine to automatically detect the source language by excluding the `source` parameter:
“`
curl -X POST “http://localhost:5050/translate” -H “Content-Type: application/json” -d ‘{
“q”: “Bonjour le monde!”,
“source”: “auto”,
“target”: “en”
}’
“`
This translates “Bonjour le monde!” into English where the server detects French as the source language resulting in:
“`
{
“detectedLanguage”: {
“confidence”: 85,
“language”: “fr”
},
“translatedText”: “Hello world!”
}
“`
At present, LTEngine remains in active development with several exciting features planned ahead. One anticipated feature includes file translation support ideally catering to popular formats like DOCX and PDF.
Nevertheless, LTEngine currently delivers top-notch AI-powered translations all processed locally on your device. Through its API endpoint capabilities, you can even construct custom translation tools or applications ensuring all data processing remains local and secure. This guarantees your data stays confidential and fully under your supervision.